Note: This essay was originally published on the University of Connecticut’s Archives and Special Collections Blog on January 14, 2019.
In my first-year writing course during the Fall 2018 at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta, my students are reading books by Second Generation New York School poets to critique and creatively reimagine concepts of youth, coming-of-age narratives, and the overlap between do-it-yourself and avant-garde aesthetics. We had already read Joe Brainard’s I Remember and Ted Berrigan’s The Sonnets, two versions of youth, memory, and selfhood constructed by male poets of the New York School, and were beginning to read Alice Notley’s Mysteries of Small Houses (1998) to extend this intertextual conversation about youth through the perspective of a female poet. While re-reading Mysteries, a book of autobiographical poems that tracks Notley’s “I” through the prismatic complexities of life and writing, I returned to her poem “Waveland (Back in Chicago)” in which Notley, challenged by the responsibilities and strictures of living inside concepts like motherhood and femininity in the mid-’70s, describes her progress of collage-making, a practice Notley continues to be devoted to.
Frozen collection of world—this is “art” I don’t
write much poetry;
I’m thinking with my hands—a ploy against fear—
I have a pile of garbage on the floor
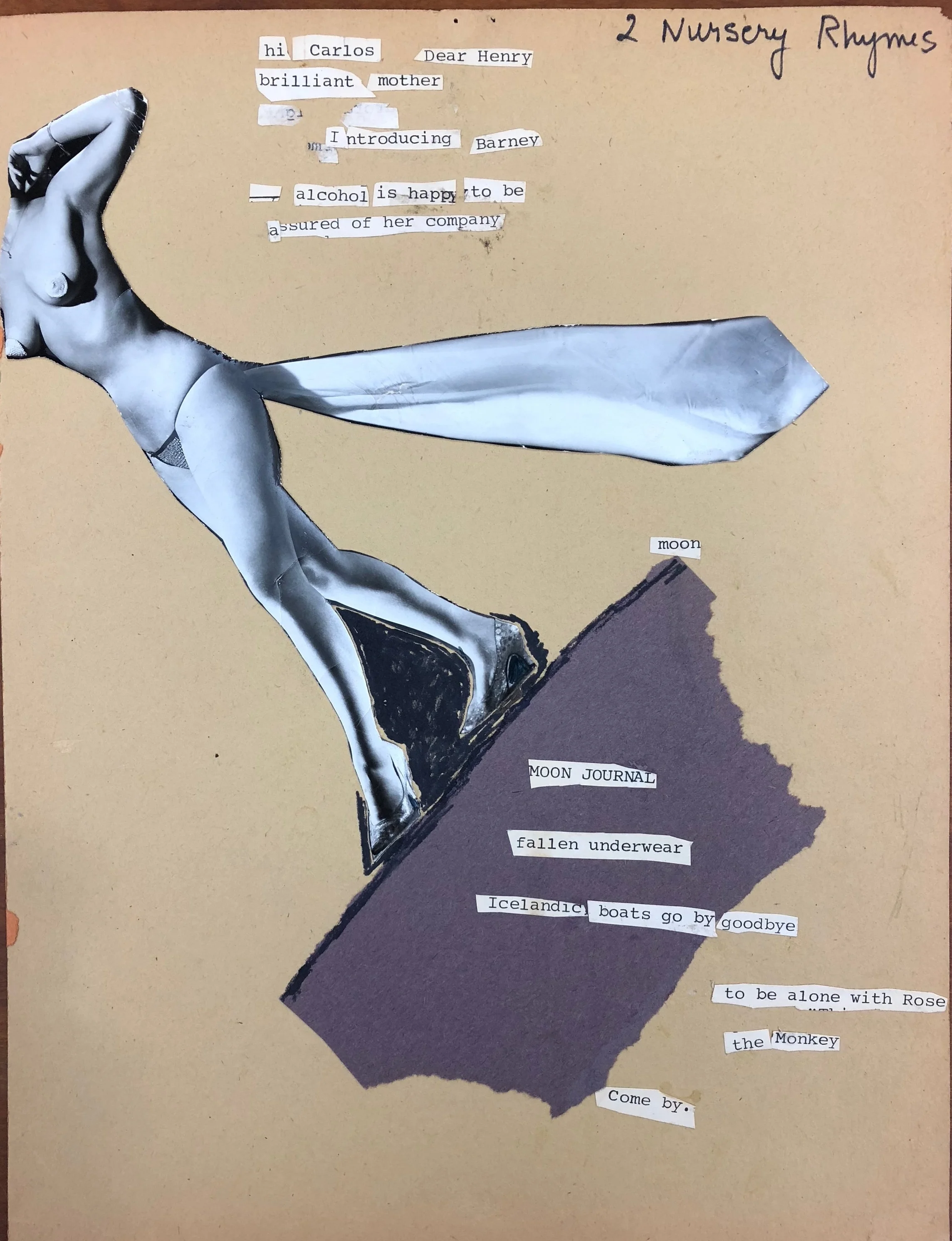
The poem then catalogs a series of collages with titles like “WATERMASTER” and “DEFIES YOU THE RHYTHMIC FRAME,” and also describes a collage composed of “a photo of a stripper I’ve named / Barney surrounded by cutout words she / dances to poetry.” Reading these lines, I remembered that I had actually just seen this very collage in Notley’s papers at the University of Connecticut. Among about a dozen collages by Notley, there was Barney herself, headless, cape trailing behind her, walking across a fragment of moon. After discussing this poem in class, I was able to show my students the collage to talk about how seeing an example of Notley’s visual art helped us think about her critiques of femininity, motherhood, and aesthetics. Students were surprised that I even had such an example to show them and immediately started to describe the effects of juxtaposing the idea of “2 Nursery Rhymes” paired with a nearly-nude woman, what it might mean for Notley to be a “brilliant mother” in association with the mythological feminine connotations of the moon, and how the epistolary gesture “hi Carlos Dear Henry” resonated with Berrigan’s The Sonnets, which is riddled with the salutation like “Dear Marge,” “Dear Chris,” and “Dear Ron.” Seeing Notley’s collage projected in front of them, pairing the material evidence of the poem’s description with a conversation about how the visual medium supplemented their reading of the text, students said they felt a different connection to the poem, to Notley’s work, and to our entire discussion that day.
Of course, none of this would have been possible without my recent visit to the archives at the University of Connecticut. Thanks to the generosity of a Rose and Sigmund Strochlitz Travel Grant, I spent a week in the papers of poets and artists like Notley, Ted Berrigan, Bill Berkson, and Ed Sanders, among others, including voluminous correspondence with Joe Brainard, Anne Waldman, Bernadette Mayer, Lewis Warsh, Ron Padgett, and a litany of other Second Generation New York School writers. Well-known for its Charles Olson Research Collection, the Thomas J. Dodd Research Center is also home to a wealth of materials associated with the New York School and is a necessary destination for any scholar of 20th century American poetry. And though a week of nonstop work in the archive allowed me to read and assess a lot of material, the sheer amount of New York School material stored at UConn, much of which has only barely begun to be utilized by scholars, meant that I was inevitably rushing through stacks of papers, quickly unfolding and refolding letters, swiftly scanning folder titles, and scratching nearly incomprehensible notes, in a frenzied, focused attempt to see and catalog as much as possible before getting back on the plane to Atlanta. All the time in the archive, like Notley’s description of collage-making in Mysteries, I’m “thinking with my hands” as I arrange, photograph, and order material in “a ploy against [the] fear” of overlooking or not knowing the full extent of what’s present in the archive. Every piece of material in the archive, like in Notley’s collage, is necessary and meaningful. This is how “a pile of garbage” becomes both art and scholarship. Starting with what you touch, a life and intelligence are animated.
Notley wasn’t the only poet whose visual artwork is held at the University of Connecticut. Take this incredible poster-size collage “Blues Bombard” (1965) by Ron Padgett with the poet’s thick, elegant cursive painted over sliced fragments of sheet music that frame a photo booth portrait of Padgett, face half-obscured, cool, and mysterious. It’s rare to find visual artwork by Padgett that isn’t a collaboration with friends like Brainard or George Schneeman, and this piece is particularly astounding both for its size and the quick, pleasing, and humorous visual narrative that follows from the newspaper clipping-title, down across the rhyming and chiding main text ”more than likely this stinks greatly,” the arrows and question marks that logically and quizzically suggest a set of correspondences, the appearance of the artist mid-gesture, and the small, humorous, non sequitur conclusion “a hole in one. THE END.” It’s a lovely piece, and entirely Padgett in its cartoonish wit and simplicity.
I was also interested to work in Ed Sanders’s papers at UConn, which includes a wealth of material from the Peace Eye Bookstore, the infamous “secret location on the lower east side” where Sanders’s mimeograph magazine Fuck You: A Magazine of the Arts was published from 1962-65 until the store was raided by the NYPD on obscenity charges. Incredibly enough, the collection includes both a handwritten note from 1964 instructing Sanders to call an FBI agent and Sanders’s January 1965 mugshot following his arrest. After Sanders defeated the charges against him, Peace Eye temporarily reopened in 1967 with a Fuck You-style gala event auctioning off “literary relics & ejeculata from the culture of the Lower East Side.” The collection includes the handwritten notecards Sanders used to identify the various items for sale in the auction, like an “iron used by rising young poets to iron the buns of W.H. Auden during the years 1952-1966,” “Allen Ginsberg’s Cold Cream Jars,” and a letter from Marianne Moore to Sanders in response to receiving a copy of Fuck You in the mail. It’s especially incredible to have copies of the material actually confiscated by the NYPD in the raid of the bookstore with the police evidence identification slips still attached, like a copy of a Joe Brainard drawing described by police as “Blue colored Headless Superman drawing with private parts exposed.”
Among collages and obscenity charges, the New York School material at UConn also runs parallel to and benefits from the archive’s already well-known collections of Frank O’Hara and Charles Olson papers. The resonance of those collections are embodied in two postcards; one from Frank O’Hara to Ted Berrigan and another from Berrigan to Charles Olson. Much can be made of the micro-lineage threads of the New American poetry and New York School that run through these three poets. Not only are Olson and O’Hara canonical energies within Berrigan’s The Sonnets, but Berrigan’s self-described “rookie of the year” arrival in American poetry occurred at the 1965 Berkeley Poetry Conference, over which Olson’s presence loomed large, and O’Hara’s work and entire aesthetic field had been a guide for Berrigan on how to live as a young poet. What’s great about the 1962 postcard from O’Hara to Berrigan is that it offers a reversal on the standard hierarchical narratives of literary tradition. Here, it’s O’Hara praising Berrigan’s poems as he invites him out for a drink and “to meet K. [Kenneth] Koch,” who would also be a New York School hero to Berrigan. Evidenced by the tape arranged on the edges of the card to harden and preserve it, Berrigan clearly treasured this correspondence from O’Hara, which due to the use of Berrigan’s full name, seems to have been their very first. One images Berrigan, then 27 years old and having just moved to New York City the year before, formally expressing his admiration for O’Hara’s poems, and this postcard is evidence of Berrigan’s devoted friendship with his interests and aesthetic sources. The August 16, 1966 postcard from Berrigan to Olson, on the other hand, reveals an already well-established and easy going correspondence with the author of The Maximus Poems and “Projective Verse,” as Berrigan, referencing the postcard’s text on the other side, writes, “Dear Charles, We’re about to beat upwind. A loon is crying tonight. Maine is full of sky,” and signs off, “Be seeing you, Ted + Sandy.” Likely having stopped in to see Olson in Gloucester, Massachusetts on the drive up to Maine with his first wife, Sandy, Berrigan is playfully following up with the elder poet only about three weeks after the death of O’Hara. Though Olson himself would die in 1970 and it’s unclear if further correspondence between the two poets exists, his “full of sky” note to Olson again shows Berrigan’s sense of intimacy with the poets whose work he respected and learned from. The archive, as it often does, is showing us how lineage, tradition, and aesthetic exchange are never abstract.
I’m looking forward to returning to the archives at the University of Connecticut to spend more time thinking through the material traces of the poets I love and study, and to continue to utilize these important and still growing collections to illustrate the ongoing importance and value both of the New York School’s second generation gems and the pedagogical, personal, and scholarly correspondence that archives allow us to develop. “I must be making my own universe / out of discards,” Notley writes in “Waveland (Back in Chicago),” and there’s a sense of that same construction of a world in the loose, wayward ephemera of the archive. What’s most fulfilling is how the process of looking and reading in the archive is always one of presence, and often magically, of being in contact with your sources.